Exploring the Dual Role of AI in Modern Cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly reshaping the landscape of cybersecurity. Its influence extends to both sides of the digital battlefield: while it empowers defenders to predict, detect, and respond to threats more effectively, it also enables attackers to launch more sophisticated and adaptive assaults. Let’s look into the transformative impact of AI on both cyber-attacks and cyber defence, highlighting the opportunities and challenges presented by this evolving technology.
The Role of AI in Cyber Attacks
Artificial intelligence is significantly transforming the landscape of cyber-attacks, presenting both new opportunities and challenges. One key development is the enhancement of attack sophistication; AI enables cybercriminals to execute more intricate and adaptive attacks that are harder to predict and prevent. Another critical impact is the automation of cyber-attacks, AI can automate tasks such as vulnerability scanning and exploit development, allowing attackers to scale their efforts and launch more attacks in a shorter time frame. The dual use of AI in both offensive and defensive capacities underscores the need for continuous innovation and vigilance in the field of cybersecurity.
AI influence and Risks Snapshot –
- Rapid Increase in AI Usage: According to various industry reports, over 35% of cyber-attacks in 2025 involved some form of AI or machine learning, up from just 18% in 2023.
- Automation of Attacks: 65% of surveyed cyber security professionals in 2025 reported seeing a significant uptick in automated, AI-powered phishing and malware campaigns
- Phishing: AI-generated phishing emails have a 40% higher success rate compared to traditional phishing campaigns, thanks to improved personalisation and language sophistication.
- Malware Development: 50% of new malware variants detected in 2025 exhibited characteristics of AI-generated code, making detection and analysis significantly more challenging.
- Deepfakes and Social Engineering: There was a 250% year-on-year increase in reported incidents involving deepfake audio or video used for fraud and impersonation in 2025.
- Attack Velocity: AI-powered attacks can breach networks in under 10 minutes on average, compared to several hours for manual techniques.
- Volume: Automated AI bots can launch thousands of attacks simultaneously, making traditional defence mechanisms less effective.
- Cost of AI-Driven Attacks: The average cost of a data breach involving AI-powered tools reached £4.5 million in 2025, a 30% increase from 2023.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): AI-enabled BEC fraud losses globally surpassed £2.1 billion in 2025, with AI tools used to mimic executive writing styles.
- Targeted Sector: The sectors most frequently targeted by AI-driven attacks in 2025 included financial services (28%), healthcare (22%), and government agencies (16%), due to the high value of data and critical infrastructure.
- Regulatory Response: New regulations are emerging globally to address the risks of AI in cyber-crime, especially in the EU and UK.
AI-powered tools can automate much of the attack process, making cyber threats more dynamic and difficult to counter. Below are some of the primary ways AI is being used to advance cyber-attacks:
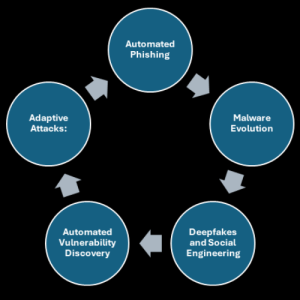
- Automated Phishing: AI can generate convincing phishing emails by mimicking writing styles and personalising content based on harvested data. Machine learning algorithms can also identify the most susceptible targets and optimise the timing of attacks for maximum impact.
- Malware Evolution: AI allows for the creation of malware that can adapt its behaviour to evade traditional detection methods. For example, AI-driven malware can analyse its environment and modify its code to bypass antivirus solutions or sandboxing techniques.
- Deepfakes and Social Engineering: AI-generated synthetic media (deepfakes) can be used to impersonate individuals convincingly in video or audio, thereby facilitating high-stakes fraud or manipulation.
- Automated Vulnerability Discovery: Attackers employ AI to scan software and systems for vulnerabilities at scale, drastically reducing the time required to find exploitable weaknesses.
- Adaptive Attacks: AI algorithms can analyse the responses of targeted systems in real time and modify attack strategies, accordingly, making them more persistent and harder to block.
AI is reshaping the world of cyber-attacks, making them more targeted, efficient, and difficult to detect. While the technology offers significant benefits for cyber defence, it also empowers malicious actors with advanced tools. Addressing the challenges posed by AI in cybersecurity will require ongoing innovation, vigilance, and collaboration across sectors.
The Role of AI in Cyber Defence
Conversely, AI is emerging as an indispensable asset for cybersecurity experts. Its capability to analyse extensive datasets and discern patterns facilitates more proactive and efficient defensive strategies. The rapid evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the domain of cyber defence. As digital threats grow increasingly sophisticated, organizations are leveraging AI-driven solutions to bolster their security infrastructures, enhance threat detection, and respond to attacks with heightened agility. This document delves into the diverse applications of AI in cyber defence, highlighting its advantages, challenges, and the outlook of this ever-evolving field.
Key applications of AI in cyber defence include:
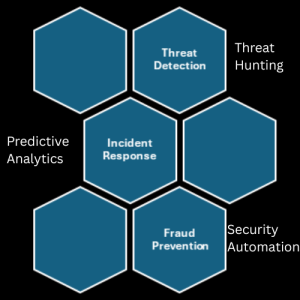
- Threat Detection: AI-powered security systems can analyse network traffic and user behaviour to identify anomalies that may indicate a cyber-attack. Machine learning models can detect previously unknown threats by recognising suspicious patterns.
- Incident Response: AI can automate aspects of incident response, such as isolating compromised devices, blocking malicious traffic, and conducting forensic analysis, thereby reducing response times and limiting damage.
- Predictive Analytics: By analysing historical attack data, AI can predict emerging threats and help organisations prioritise their security efforts accordingly.
- Fraud Prevention: Financial institutions and e-commerce platforms use AI to detect fraudulent transactions in real time by identifying subtle deviations from normal behaviour.
- Security Automation: AI enables the automation of routine security tasks, freeing up human experts to focus on more complex issues and improving overall efficiency.
The role of AI in cyber defence is set to expand as technology evolves. Future developments may include more sophisticated autonomous response systems, improved collaboration between human analysts and AI, and the use of AI to anticipate and prevent emerging threats. However, ongoing research and investment will be essential to ensure that AI remains effective against increasingly cunning adversaries.
AI is revolutionising cyber defence, offering powerful tools to detect, respond to, and prevent cyber threats. While challenges remain, its benefits are undeniable, and its role in safeguarding digital assets will only grow in importance. Organisations must continue to invest in AI-driven security solutions, adapt to new threats, and address ethical considerations to fully realise the potential of AI in cyber defence.
Challenges and Risks while using AI:
While AI offers significant benefits, it also introduces new risks and challenges in both attack and defence contexts:
- Defence Mechanism: AI is driving a technological arms race between attackers and defenders. As defences become more advanced, cybercriminals continually enhance their methods to breach systems.
- False Positives/Negatives: While AI systems offer significant advantages in cybersecurity, they are not without flaws. These systems can produce false positives, flooding security teams with excessive alerts, or false negatives, which result in genuine threats being overlooked.
- Bias and Adversarial Attacks: Attackers who comprehend the internal workings of AI algorithms can exploit these models, leading to incorrect classifications or complete evasion of detection.
- Skill Gaps: Implementing and managing AI-driven cybersecurity solutions requires specialised skills, creating a demand for new expertise in an already stretched field.
Artificial Intelligence is a double-edged sword in the realm of cybersecurity. It is revolutionising both the offensive and defensive sides of cyber warfare, offering unprecedented capabilities to both attackers and defenders.
Recommendations to overcome Risks and Challenges while using AI:
To overcome the challenges and risks associated with AI in cybersecurity, organisations should adopt a multi-faceted approach. Firstly, investing in continuous training and development will help bridge skill gaps, ensuring cybersecurity professionals remain proficient in the latest AI technologies and threat landscapes. Collaboration with academic institutions and industry partners can also foster knowledge exchange and innovation.
- Invest in ongoing training to bridge skill gaps and keep cybersecurity teams up-to-date with the latest AI technologies.
- Collaborate with academic and industry partners to encourage knowledge sharing and innovation.
- Use layered security approaches, combining AI with traditional methods and human oversight to reduce false positives and negatives.
- Regularly update and test AI models to improve accuracy and minimise misclassifications.
- Validate models with diverse data, conduct adversarial testing, and enhance transparency using explainable AI tools to counter bias and adversarial attacks.
- Implement strong ethical frameworks and governance to ensure responsible AI use, balancing innovation with privacy and security.
- Maintain investment in research and work with regulatory bodies to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
As AI technology continues to advance, it is crucial for organizations to remain vigilant by investing in cutting-edge security solutions and enhancing their workforce’s skills. This proactive approach will help them keep up with an ever-evolving threat landscape. The future of cybersecurity hinges on our ability to leverage AI responsibly and ethically, ensuring that our efforts are geared towards defence rather than offense. By doing so, we can create a safer digital environment for all.
Written by: Kavitha Srinivasulu
Company: TCS
Designation: Program Director–Cyber Security & Data Privacy : BFSI
About the Author: Experienced Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Leader with overall 22 years of experience focused on Risk Advisory, Data Protection and Business Resilience. Demonstrated expertise in identifying and mitigating risks across ISO, NIST, SOC, CRS, GRC, RegTech and in emerging technologies with diverse experience across corporate and Strategic Partners. Possess a solid balance of domain knowledge & smart business acumen ensuring business requirements and organizational goals are met.
Disclaimer:
“The views and opinions expressed by Kavitha in this article are solely her own and do not represent the views of her company or her customers.”